
Paper Notes 2023
2023-7月@8月@9月
Some phrases
As the ore product
ore n.矿;矿石,矿砂;
Plateau : n.高原;平稳时期,稳定水平;停滞期; v.进入停滞期;达到平稳状态;
permafrost strata 永久冻土地层
within the system due to the variety of substances, the inhibitory effect of inhibitors will vary due to multiple factors
thus far 迄今为止
adsorption and stereo-hindrance effects. 吸附和立体位阻效应。
In sharp contrast 形成鲜明对比
The heat consumption for this dynamics process can be replenished by the bulk water and silica phase in our simulations.
In this regard, 在这方面:表示在某个特定的方面或情况下。
the soaring cost of hydrate inhibitors
- soaring : *adj.*翱翔的;高耸的;猛增的
it would be of great concern. 这将引起极大的关注。
and so forth
a variety of
sustainable technologies 可持续性技术
shed light on 阐明;使…清楚地显出
- illustrate、clarify
This may be due to the fact that there are fewer polar atoms in aromatic hydrocarbons and glial molecules
as corroborated by the research of Kang et al. Kang等人的研究也证实了这一点。
水合物钻井
- 由于水合物地层强度较低,目前应用最广泛的水合物地层钻井方法——压力控制 和 温度/压力控制方法,不能保证钻井安全,易导致地面套管下封前钻井液泄漏或水合物不可控解离
Bernal–Fowler 冰规则(Bernal–Fowler ice rule)
用于描述某些晶体中的离子或分子的排列规则。该规则适用于一些晶体结构中存在的离子或分子有两种不同的位置,并在这些位置上交替排列的情况。
根据 Bernal–Fowler 冰规则,当存在交替排列的离子或分子时,每个离子或分子都应该被其最近的邻居包围或接触,形成一种稳定的排列模式或者称为凝聚态。
这个规则得名于科学家J.D. Bernal和R.H. Fowler,他们提出了这个规则来解释冰的晶体结构中水分子的排列方式。尽管该规则最初是对冰的解释,但后来发现它还适用于其他晶体结构,尤其是具有离子交替排列的晶体。
ChatGPT学术版
tortuosity
Quartet Structure Generation Set method (QSGSM)
- Generate random porous media with Quartet Structure Generation Set (QSGS) method.
1 | git clone https://github.com/Jeff-Hugh/GenPorMed.git |
沉积物内水合物三种典型的赋存状态

Fuel 353 (2023) 129032
pnextract
多孔介质微ct图像的孔隙网络提取
文献:
Volumetric Lattice Boltzmann Method (VLBM)
- GPU-accelerated volumetric lattice Boltzmann method for porous media flow - ScienceDirect
- Unified mesoscopic modeling and GPU-accelerated computational method for image-based pore-scale porous media flows - ScienceDirect
- A greyscale volumetric lattice Boltzmann method for upscaling pore-scale two-phase flow - ScienceDirect
Thermal fluidization index (TFI)
热流化指数(TFI)可以衡量动态过程中弱相互作用的稳定性。
$TFI=\frac {std(rho)} {avg((rho))}$
$avg(rho)$是整个轨迹的平均密度,$std(rho)$是整个轨迹密度的方差。
J. Am. Chem. Soc., 132 (18) (2010), pp. 6498-6506,
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2023, 370: 121008.
Mass Transport Deposits (MTDs)
- 是一种地质术语,用于描述海底沉积物的运移沉积现象。MTDs 是指大规模沉积物在海底坡度较陡的区域发生崩塌或滑动后,向下坡移动并在海底堆积形成的沉积物体。这些沉积物体通常包括岩屑、泥浆、碎屑和水合物等。
- MTDs 可能发生在大陆坡、河口三角洲、海底峡谷和海底扇等地形复杂的区域。这些沉积物体的形成可能是由于地震活动、重力滑坡、海底流体渗透导致沉积物流动等因素引起的。
- MTDs 不仅对地球科学研究有着重要意义,还对海底资源勘探和开发具有重要影响。了解和研究 MTDs 可以帮助我们理解海底地质过程、预测地质灾害风险并评估潜在的油气和矿产资源。
Bottom Simulating Reflector (BSR)
- 是指一种地球科学术语,用于描述海底地震勘探中的一种地质特征。
- 简单来说,BSR 是一种在海底地形中反射声波的地层。
- 它通常指示着在深水海底和沉积物之间存在着天然气水合物的存在。
- 当声波遇到天然气水合物的边界时,会发生反射,形成BSR。
- 因此,BSR 的存在可以作为检测天然气水合物存在的指标之一。这对于天然气水合物的勘探和开发具有重要意义。
热力学抑制剂浓度对水合物分解抑制的影响

- 实验证明低浓度热力学抑制剂,例如乙二醇(EG),会抑制水分合分解,高浓度下促进分解
水合物井筒模型:
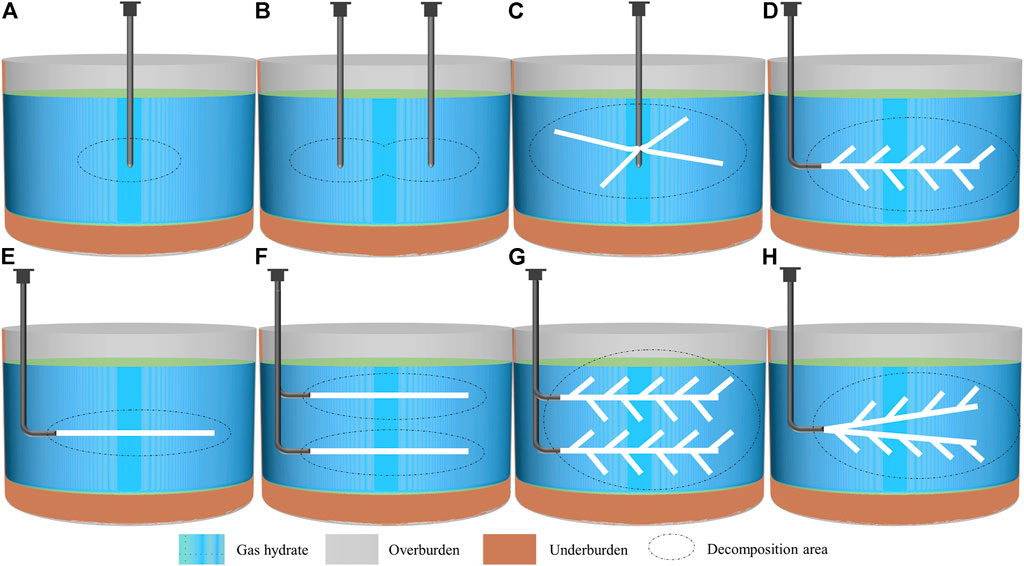
- (A)单口直井、(B)双口直井、(C)径向水平井、(D)鱼骨井、(E)单口水平井、(F)双口水平井、(G)双鱼骨井、(H)双分支分支分支水平井。
LSTM (long short-term memory )
Energy 282 (2023) 128337
LSTM is a deep learning algorithm that is able to predict future events by learning features from historical data.
LSTM has been successful in language modeling, speech-totext transcription and machine translation
The LSTM neural network model ML model is a sequential model including head-to-tail, linear stacking model without bifurcation.
为什么甲烷水合物分解后,很多甲烷分子吸附在了亲水的石英表面
Fuel 258 (2019) 116106
- Several factors may contribute to the formation of methane nanobubbles on hydrophilic silica surfaces.
- The first is that the adsorption behavior of $CH_4$ on the solid surface with silanol groups in $CH_4-H_2O-SiO_2$ three phase system is more complicated than $CH_4-SiO_2$ or $H_2O-SiO_2$ two phase systems; this process is affected by temperature, pressure and water content. Recently experimental work shows that at a certain water content, confined water molecules (water within the pores) can promoted the adsorption of $CH_4$ by forming deeper adsorption potential energy wells on hydrophilic silica surfaces, making the system more stable.
- The second effect is that the kinetics factor may be important. During the decomposition of hydrates, methane molecules did not immediately release from the silica nanopore to the bulk phase, instead, they aggregate in the silica nanopore and form bubbles on the surface.
水合物与岩石表面之间的缓冲水
Fuel 258 (2019) 116106
- due to the fact that the bound water on the surfaces of semimetal grains cannot be 100% converted into hydrate both in simulations and experiments, and this thin water layer could relieve the mismatch between hydrate and silica two solid lattices.
水合物分解的两个步骤
Fuel 258 (2019) 116106
- first, the enhanced diffusive behaviors of the host water molecules in the hydrate crystals lead to unit cell size increases and distortions that ultimately break down the lattices;
- second, methane molecules escape from these incomplete cages and aggregate
钻井液的功能
清洗:Cleaning the Hole;
冷却和润滑:Cooling and Lubricating Drill String;
排出岩屑:Lifting Cuttings to the Surface;
获得地层信息:Carrying Information about Formations;
稳定井筒:Stabilizing Wellbore;
控制地层压力:Controlling Formation Pressure;
?:Suspending Cuttings;
水合物钻井面临的挑战
Arabian Journal of Chemistry (2023) 16, 105068
低温高压下,钻井液黏度增加,钻井困难;
The high pressure and low temperature environment of offshore drilling increases the viscosity of drilling fluid, resulting in increased difficulty in regulating the low temperature rheology of drilling fluid and making the drilling process difficult.
钻井液入侵水合物层,导致水合物分解,井壁失稳;
The drilling fluid invades the natural gas hydrate formation, breaking the original state of the stable existence of natural gas hydrate, and the decomposition of natural gas hydrate leads to wellbore instability.
近井水合物分解,生产管道、阀门内二次水合物形成引起的堵塞问题;
Decomposition of natural gas hydrates in the vicinity of near wells, and blockage problems such as secondary hydrate formation in production pipelines and valves after decomposition of free natural gas
First-order or second-order phase transformation
第一阶相变(First-order phase transformation)和第二阶相变(Second-order phase transformation)是描述物质在不同条件下发生的相变类型的术语。
第一阶相变: 第一阶相变是指在相变过程中,物质的热力学状态会经历一个明显的跃迁。在这种相变中,物质的熵和焓会发生突变,导致相变点处出现明显的跃迁。典型的第一阶相变包括固体和液体之间的相变(如熔化和凝固)、液体和气体之间的相变(如沸腾和液化)。在第一阶相变中,物质在相变点处会同时存在两种相态,而且相变过程中的温度和压力保持不变。
第二阶相变: 第二阶相变是指物质在相变过程中没有明显的热力学跃迁,其熵和焓的变化是连续的。在这种相变中,物质的某些物理性质会发生突变,如磁性、电导率或比热容等。典型的第二阶相变包括铁磁性相与顺磁性相之间的相变、液晶相变、超导相变等。与第一阶相变不同,第二阶相变在相变点处不会同时存在两种相态,而是通过连续的变化逐渐转变。
总结来说,第一阶相变是具有明显热力学跃迁的相变,其过程中熵和焓发生突变,物质在相变点处同时存在两种相态。而第二阶相变是连续的相变,其过程中熵和焓变化连续,物质在相变点处只存在一种相态,但某些物理性质可能发生突变。


